🌿 Beyond Batteries: Why Green Hydrogen is the Energy We’ve Been Waiting For
Published on June 16, 2025 by Krish Pathak

Why It Matters
Green hydrogen is important because it can cut pollution in hard-to-clean sectors. Factories, trucks, ships, and planes need strong fuels. Electricity is not always enough for them. For example, steel and cement plants use high heat, which electricity can't always provide. Hydrogen burns hot and clean. It can replace coal in these industries. Also, fuel made from hydrogen can power trucks and trains that travel long distances. Unlike batteries, hydrogen can be filled up quickly and carried in tanks. This makes transport easier and faster. Green hydrogen can store energy too. When there’s extra solar or wind power, it can make hydrogen. Later, that hydrogen can make electricity again. This helps during cloudy days or nights when solar panels don’t work. So, green hydrogen is more than a fuel. It’s a clean storage system, a replacement for dirty gases, and a tool to help stop climate change.
Current Global Trends
Many countries are now racing to become leaders in green hydrogen. Europe, Australia, Japan, India, and the United States are building large green hydrogen projects. These countries see hydrogen as a way to secure clean energy and create new jobs. In Europe, several nations are linking hydrogen plants through shared pipelines. Japan is focusing on hydrogen for cars and buses. Australia has started exporting green hydrogen to nearby countries. India has launched a national mission to boost green hydrogen production. Globally, over 1,000 hydrogen-related projects are now active or being planned. Most focus on building electrolyzers — the machines that split water. These projects are increasing in number and size every year. However, green hydrogen still makes up only a tiny part of the world’s total energy use. Most hydrogen today is still made from fossil fuels. But the shift has begun, and it’s gaining speed.

Breakthrough Technologies
Technology is moving fast in green hydrogen. The biggest area of growth is in electrolyzers. These machines are getting cheaper and more powerful. Some new types use less water or work at higher temperatures, which boosts their efficiency. Solar panels and wind turbines are also improving. They are now making more power for less money. This is helping green hydrogen become more affordable. Another big change is in hydrogen storage. Companies are developing tanks that hold more gas safely. Some are testing liquid hydrogen, which can be stored in very cold containers. Pipelines made just for hydrogen are being built too. These will carry hydrogen from places with lots of sunlight or wind to cities that need clean energy. Some companies are combining hydrogen with other gases to create green fuels for planes and ships. These new fuels work like oil but don’t pollute the air.

Top Companies Leading Innovation
Many global companies are now investing in green hydrogen. Some are building massive electrolyzer plants. Others are developing engines and fuel cells that run on hydrogen. Big energy firms are turning their focus from oil and gas to clean hydrogen. These companies are working with car makers, airlines, and shipping firms to develop hydrogen-powered vehicles. Several new startups are also making progress. They are creating advanced technologies like small electrolyzers, hydrogen batteries, and smart storage systems. In Asia, automakers are testing hydrogen trucks and buses. In Europe, companies are blending hydrogen into the gas used for heating homes. In the U.S., tech firms are building hydrogen hubs with partners from across industries. Together, these companies are shaping a new energy market that runs on clean gas instead of fossil fuels.

Challenges Faced
Despite the promise, green hydrogen faces major hurdles. The first is cost. Making hydrogen from water using clean electricity is still expensive. It can cost three to five times more than making hydrogen from fossil fuels. Transporting hydrogen is tricky too. It needs special tanks and pipes. It also leaks more easily than natural gas. This makes storage and transport harder and more expensive. Another challenge is infrastructure. Most countries don’t have hydrogen pumps at gas stations or enough pipelines to move it around. These systems need to be built from scratch. Also, making hydrogen uses a lot of water. In dry regions, this could be a problem. Careful planning is needed to make sure water use stays safe. Finally, there are safety concerns. Hydrogen is very flammable. Extra steps are needed to handle it safely at every stage.
Government Policies or Incentives
Governments are stepping in to support green hydrogen. Many have announced funding plans and rules to help companies build and use hydrogen systems. In some countries, governments give money to build electrolyzers or hydrogen buses. Others offer tax cuts or pay companies based on the clean energy they produce. Many nations have set hydrogen targets. These are goals for how much green hydrogen they want to make or use in a few years. Some places are working on hydrogen laws. These rules will guide how hydrogen is made, stored, and transported safely. Through these actions, governments hope to cut pollution, lower energy costs, and create green jobs.

Future Outlook
Green hydrogen is expected to grow fast in the coming years. Falling technology costs and more government support may help it compete with fossil fuels. Major oil and gas firms are shifting towards hydrogen. Car and truck makers are building new hydrogen models. Countries are planning to trade green hydrogen like oil and gas. More projects are moving from paper plans to real construction. Ports, factories, and airports are starting to adopt hydrogen in their systems. Hydrogen is also gaining a place in global climate plans. Many nations include green hydrogen in their long-term clean energy goals.
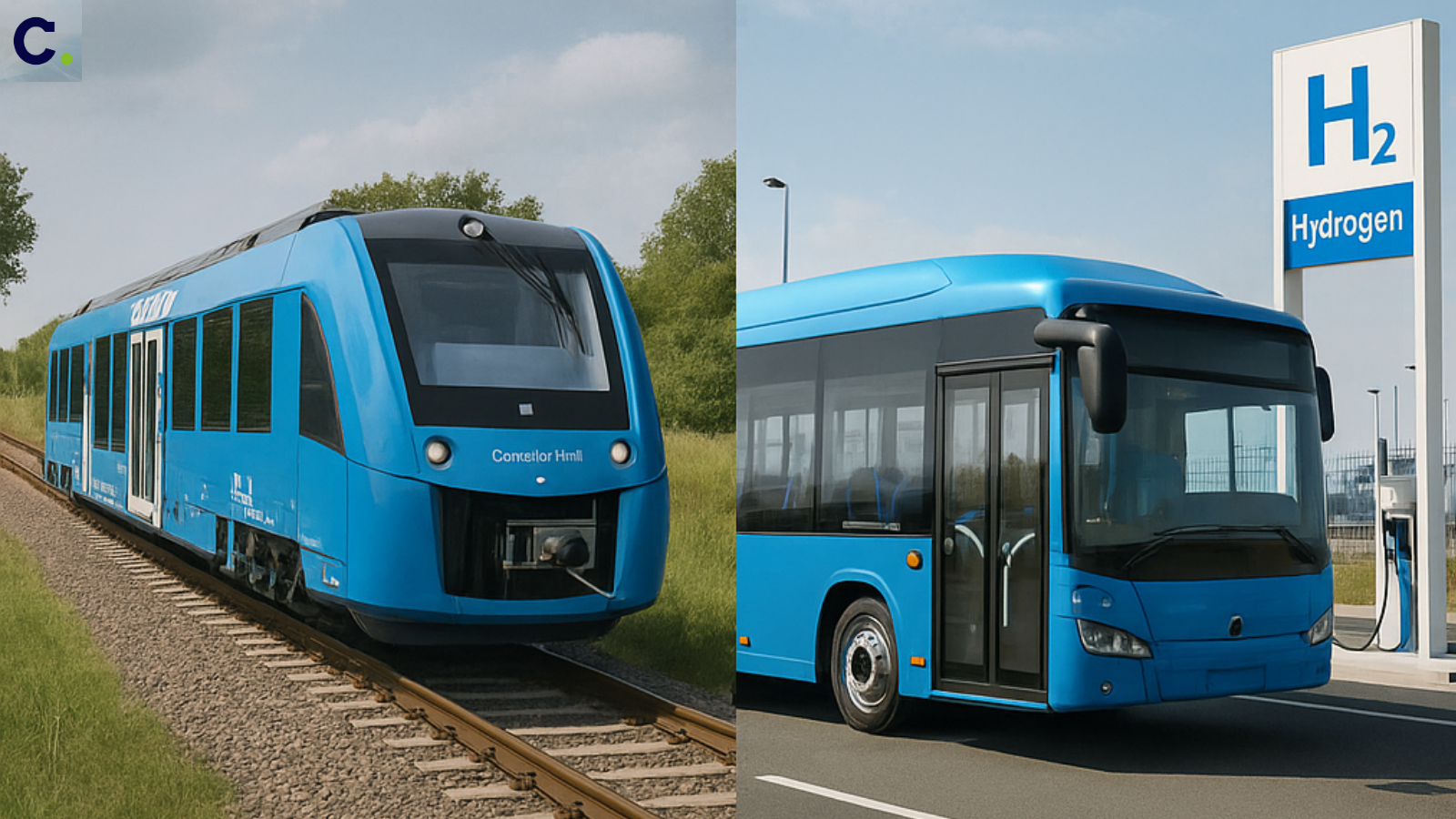

Real-World Applications
Green hydrogen is already being used in real-life situations. In Germany, hydrogen trains carry passengers with zero emissions. In South Korea, hydrogen buses are replacing diesel ones. In the Netherlands, factories are using hydrogen to make steel without coal. Airlines are testing hydrogen-powered planes. Some shipping companies are designing ships that run on hydrogen-based fuel. In remote areas, hydrogen power systems are helping keep the lights on. These systems store solar energy as hydrogen, which can later turn back into electricity. Hydrogen fuel stations are popping up in cities worldwide. Cars that run on hydrogen are filling up in minutes — just like regular cars — but without the smoke.

Conclusion & What Lies Ahead
Green hydrogen is reshaping how we think about energy. It offers a clean, powerful, and flexible option for industries that are hard to clean with electricity alone. Although challenges remain, progress is happening fast. The world is building the tools, the plants, and the networks needed to make green hydrogen part of everyday life. Its growth shows how innovation, policy, and industry can work together to create cleaner, better solutions for our planet.